The thickening mechanism is that the hydroxyl groups on the organic thixotropic molecules interact with the appropriate groups in the system rather than chemically cross-linking (Figure 13).
Thickeners of this type can be applied to many solvent-based inks and UV-curable ink systems and can impart good rheological properties to inks (Table 1).
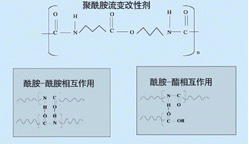
Amino-containing polyesters and polyamides can be applied to the thickening of ink overcoats. Recent studies have shown that these thickeners can provide thermoformable inks with excellent rheological properties (Figure 14).
Thickeners of this type can be applied to many solvent-based inks and UV-curable ink systems and can impart good rheological properties to inks (Table 1).
Amino-containing polyesters and polyamides can be applied to the thickening of ink overcoats. Recent studies have shown that these thickeners can provide thermoformable inks with excellent rheological properties (Figure 14).
Acrylic Thickeners (ASE and HASE)
Such thickeners are mainly polyacrylic acids copolymerized with carboxylic acids, as well as hydrophobically modified polyacrylic acids. When the aqueous system is acidic, such thickeners do not produce any thickening effect. However, when the carboxylic acid group is neutralized with a base, its molecular structure expands to produce a thickening effect.
Such thickeners are mainly polyacrylic acids copolymerized with carboxylic acids, as well as hydrophobically modified polyacrylic acids. When the aqueous system is acidic, such thickeners do not produce any thickening effect. However, when the carboxylic acid group is neutralized with a base, its molecular structure expands to produce a thickening effect.
ASE and HASE are commonly used in aqueous systems, including lithography, inkjet printing, and letterpress printing (Figure 15).
The HEUR and PEPO associative thickener HEUR (hydrophobically modified polyurethane) is formed by reacting isocyanates with diols and hydrophobic groups. The molecular structure of the HEUR comprises a hydrophilic polyoxyethylene polyether and a hydrophobic alkyl or aryl moiety, the hydrophilic and hydrophobic segments being linked by isocyanate and urethane groups. The major component of the hydrophilic segment is a polyether structure such as polyethylene glycol and its derivatives (Figure 16).
PEPO (polyether polyether) thickener molecules are grafted with hydrophobic aliphatic segments, but since the polyol is more hydrophilic, the PEPO thickened ink exhibits more Newtonian fluid properties ( Figure 17).
The HEUR and PEPO associative thickener HEUR (hydrophobically modified polyurethane) is formed by reacting isocyanates with diols and hydrophobic groups. The molecular structure of the HEUR comprises a hydrophilic polyoxyethylene polyether and a hydrophobic alkyl or aryl moiety, the hydrophilic and hydrophobic segments being linked by isocyanate and urethane groups. The major component of the hydrophilic segment is a polyether structure such as polyethylene glycol and its derivatives (Figure 16).
PEPO (polyether polyether) thickener molecules are grafted with hydrophobic aliphatic segments, but since the polyol is more hydrophilic, the PEPO thickened ink exhibits more Newtonian fluid properties ( Figure 17).

The thickening mechanism of HEUR and PEPO is the interaction of the hydrophilic groups in the thickener molecules with the hydrophilic groups in the ink formulation and the association of the hydrophobic groups of the thickener with some components in the ink composition. These effects increase the viscosity of the system by allowing thickeners and pigment particles and latex particles to form a continuous network in the ink system (Fig. 18). (To be continued)
Dinining Chair ,Nice Dining Chairs,Cute Dining Table Set,Dinner Room Chairs
Feat Top International(China) CO.,LTD , https://www.ft-project.com