2. The properties of the substrate. Paper is the most used substrate in printing. In general, non-coated paper has a loose structure, a rough surface, and strong absorptivity. The use of osmotic drying as the main, oxidative polymerization and drying supplemented by ink printing on it, not only can accelerate the ink on the paper on the fixation, but also with the oxygen molecules in the air have more opportunities to contact, the drying rate of the print faster; On the contrary, the coated paper, which has a tight structure and a smooth surface, has a slow drying rate.
At present, most of the coated paper is printed with a glossy resin type ink, which uses the absorption effect of the paint layer to increase the drying speed of the print. Bright resin ink, the main component is phenolic resin, tung oil, linseed oil and high boiling point kerosene boiling point 250 °C ~ 300 °C range. After the ink is transferred to the paper, due to the capillary action of the coating layer, the high-boiling kerosene penetrates quickly into the interior of the paper. As a result, the concentration of the resin in the binder increases, the viscosity increases, the ink thickens, and the secondary binding force between the pigment particles increases. The ink remaining on the surface of the paper forms a semi-solid, smooth and glossy gel-like film, which accelerates the drying speed of the print.
The pH of the paper has a great influence on the drying of the printing. The greater the acidity, the more severe the impediment to the destruction of oxidative polymerization. Experiments have shown that when the room temperature is kept at 20°C and relative humidity is 75%, printing is done with an offset paper with a pH of 5.4. The drying time for blotting is about 30 hours; if printing is done with an offset paper with a pH of 4.4, it takes 80 hours. Imprinting can be dry. On the other hand, printing with an offset paper having a pH higher than 8 allows the print to dry quickly in any temperature and humidity environment.
The moisture content of the paper itself also affects the drying of the print. Papers with high water content have reduced strength, the paper becomes fluffy, the fibers are in a relaxed state, and some capillaries are blocked by water molecules. Therefore, the intermolecular attraction force is weakened, and the penetrating power of the ink from the capillary to the paper is attenuated. The oxygen absorption also decreases, delaying the drying time of the blot.
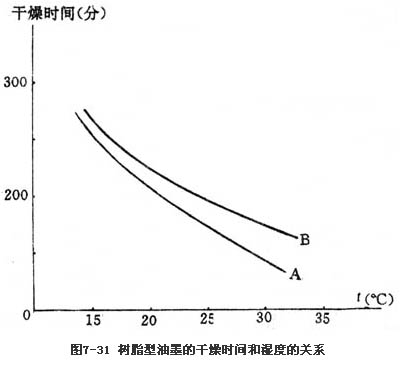
3. Temperature and humidity. The humidity in the printing shop increases, the movement of the material molecules is accelerated, the generation of oxides is promoted, the induction period of the oxidative polymerization reaction is shortened, and the drying speed of the imprinting is improved. Figure 7-31 is an experimental plot of two oxidative polymerization dried resin inks, drying time and humidity. As can be seen from the figure, as the temperature increases, the ink drying time decreases and the drying speed increases. In summer, the ink can dry quickly even without driers. However, in the winter, it is necessary to add an appropriate amount of driers to allow the ink to dry in time.
Humidity in the printing shop increases, the mobility of air oxygen molecules decreases, and the amount of dry vegetable oil absorbed by oxygen decreases, delaying the speed of oxidative polymerization drying. Figure 7-32 shows the experimental curves of the relationship between the drying time and relative humidity for the four inks of yellow, magenta, cyan, and black. From the curves it can be seen that when the relative humidity is lower than 60%, the change of humidity has no obvious effect on the ink drying. However, when the relative humidity is 90%, the drying time of the ink is greatly increased, and the ink dries slowly.
In addition, when the humidity of the workshop increases, the moisture content of the paper increases accordingly, and the result also hinders the drying of the ink. Figure 7-33 shows the relationship between drying time and relative humidity for several types of paper. It can be seen from the figure that, in the case of advanced calendered paper and coated paper, the change in humidity has little effect on the drying speed, but non-coated papers such as offset and bond papers, at low humidity (relative humidity below 50%), Can still dry quickly, but in the high humidity printing conditions, the ink must be added in the right amount of dry oil, otherwise there will be poor printing ink failure.

4. Other factors that affect ink drying. When the ink is transferred to a paper surface with an absorbent substrate, if the ink layer is thick, the ink in the surface layer and the oxygen in the air act to form a solid film rapidly. This film prevents the oxygen in the air from flowing into the ink layer. The middle enters. In addition, there is a limit to the penetration of the paper. When the ink layer is too thick, only the ink on the bottom of the sticker is easy to penetrate, while the ink in the intermediate layer can only rely on the oxidative polymerization and drying. Due to the lack of oxygen molecules, the drying speed is slow. As a result, the entire ink layer is difficult to completely dry. Therefore, controlling the thickness of the ink layer not only relates to the effect of the print tone and color reproduction, but also is very important for the drying of the print.

White ink or diluting agent (also known as Weili oil) is the main material of light ink with ink, composed of Al(OH)3 (aluminum hydroxide) and binder. Aluminum hydroxide itself is not easy to dry, it also has adsorption effect on driers. When the white ink dilutes the ink, the original driers in the ink tend to lose the drying effect, which reduces the drying speed of the print.
During the printing process, when the paper is powdered off or a hair failure occurs, a certain amount of release agent must be added to the ink to reduce the adhesiveness of the ink. The main components of the detackifier are non-drying oils and waxes. The specific gravity is relatively small. If it floats on the surface of the ink layer, the oxidative polymerization reaction of the chain material in the ink is hindered, and the ink drying speed decreases.
After printing the finished product into a stack, the molecular oxygen needed for the drying of the printed sheet can only be obtained from the air infiltrating the edge of the printed sheet. If the area of ​​the printed sheet is large, the surface of the substrate is smooth, and the weight of the printed sheet is high, and the air is hardly in contact with the ink on the printed sheet.
Because of the lack of oxygen supply, blotting must be slow, especially in the middle of the printed sheets. Drying the blots is more difficult. Therefore, a large area of ​​printed sheets should not be piled up too high. After a certain period of time, the printed sheets should be gently shaken to make them breathable, and the contact between ink and air should be increased to accelerate the drying of the ink.
Hanging Hooks,Hanging Hook,Wall Hooks For Hanging,Decorative Hanging Hooks
Jiangmen Jianghai Jianshang Houseware Co.,LTD. , https://www.jm-jianshang.com